“The problem with the lionfish is it’s like Darwin’s nightmare,” marine biologist Oliver Steeds told PBS NewsHour. Steeds is the mission director of Nekton, whose new nonprofit RISE (Robotics in the Service of the Environment) is developing a robotic lionfish exterminator. Nekton’s mission is to use exploration and science to focus the world’s attention on the health of the deep ocean.
Lionfish are native to the Indo-Pacific but fish hobbyists around the world have been attracted to their striking patterns and spines since the 1980s. Scientists think these pet owners began to release their adult lionfish into the Atlantic, where the fish thrived, bred, and spread up the coast to Maine, throughout the Gulf of Mexico, and down to Panama.
Small, native fish don’t recognize the invasive lionfish as a threat and, with their voracious appetite, lionfish tend to overeat. Plus, lionfish lack natural predators in the Atlantic, resulting in marine ecosystems with an unregulated and very deadly species.
“Lionfish are chowing their way through the food chain,” Steeds said, ”because they don’t have any predators.”
A number of initiatives have made it their mission to hunt down lionfish, offering incentives to spear fisherman who target the species. These efforts have been effective in the shallows, but researchers have found that most lionfish live 200 feet beneath the surface — too deep for the average sport diver.
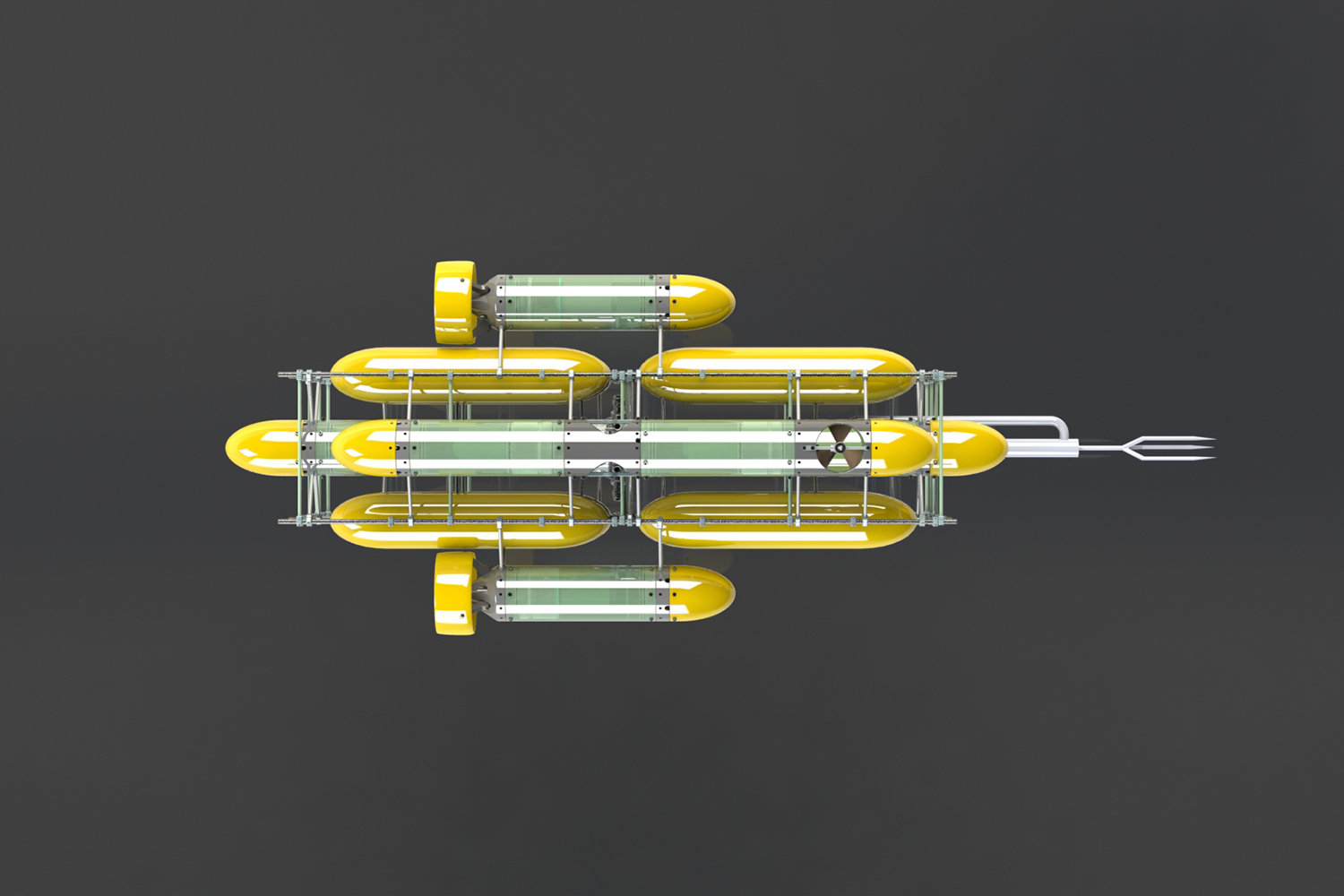
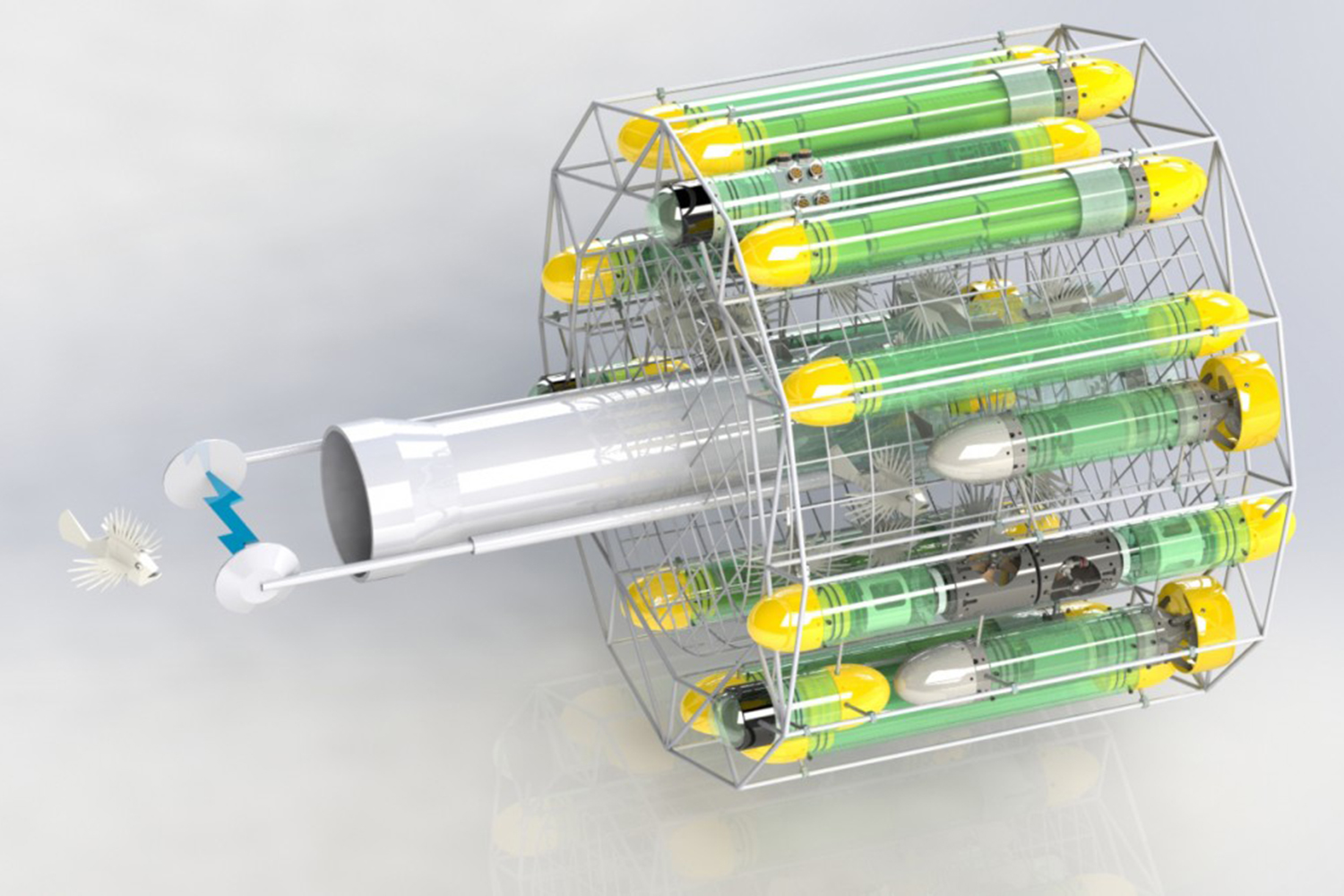
So Nekton and reef ecologist Gretchen Goodbody-Gringley are developing a robotic terminator, which will be designed to target and eliminate lionfish at all depths.
RISE is currently considering two designs for the robot, which is still in its development phase. One entails a speargun and the other utilizes a pair of electrodes that kill or stun the lionfish with an intense current running between them. Since the lionfish are rarely at risk from predators in the Atlantic, they don’t seem to budge when mock robots have approached them. And the direct current between the two electrodes ensures that native fish around the robot won’t get zapped.
Although the prospects of RISE seem promising, scientists are looking forward to trials before giving the machine their full support.
“We are very excited about the application of robotics in marine conservation,” ocean ecologist James Morris told PBS. “But whether or not a lionfish-killing robot is practical or not is yet to be determined.”