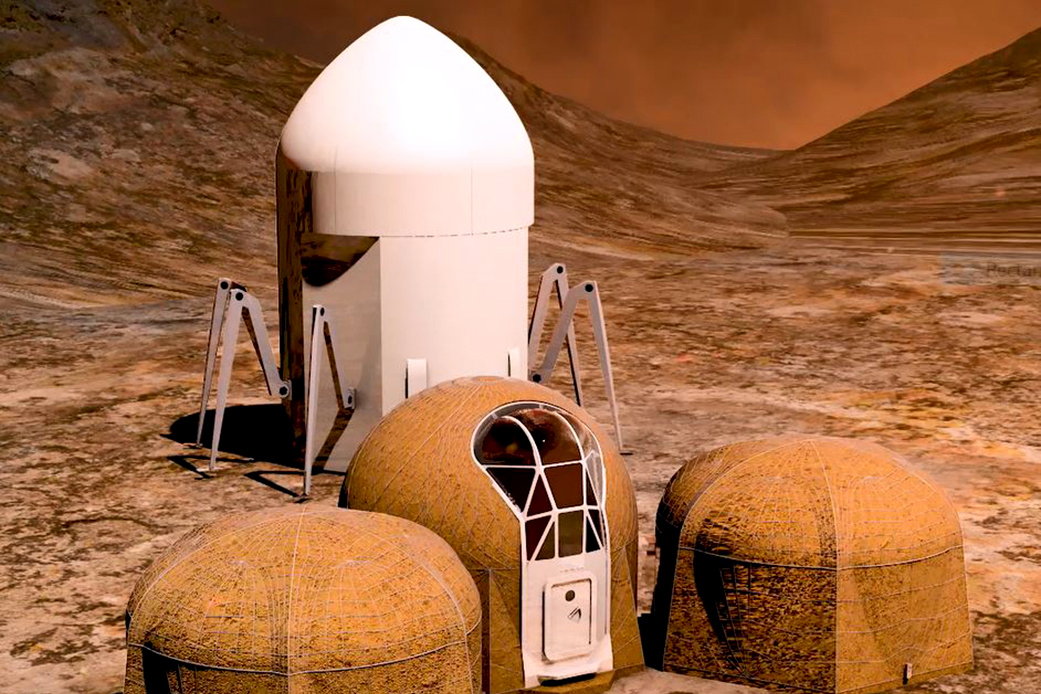
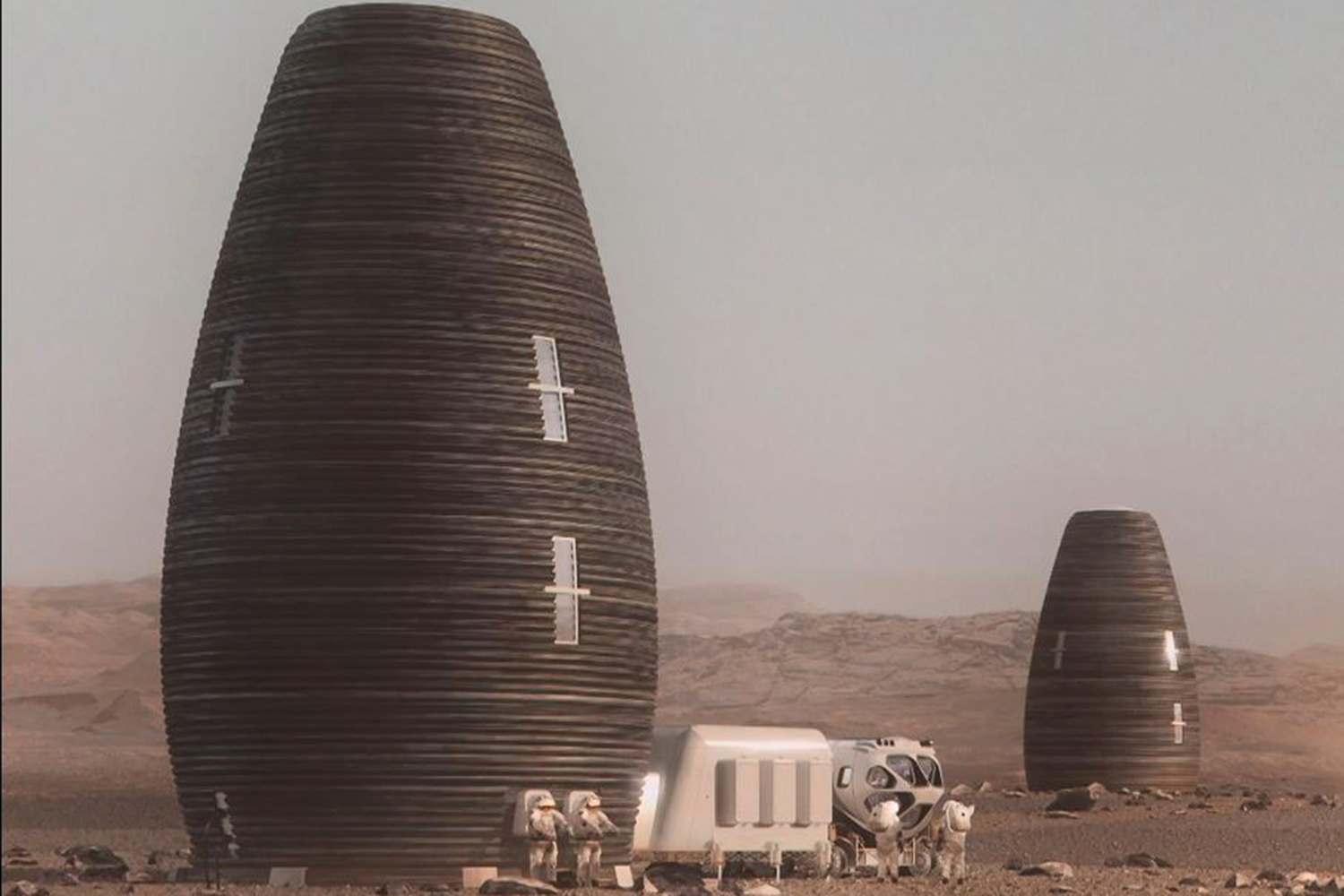
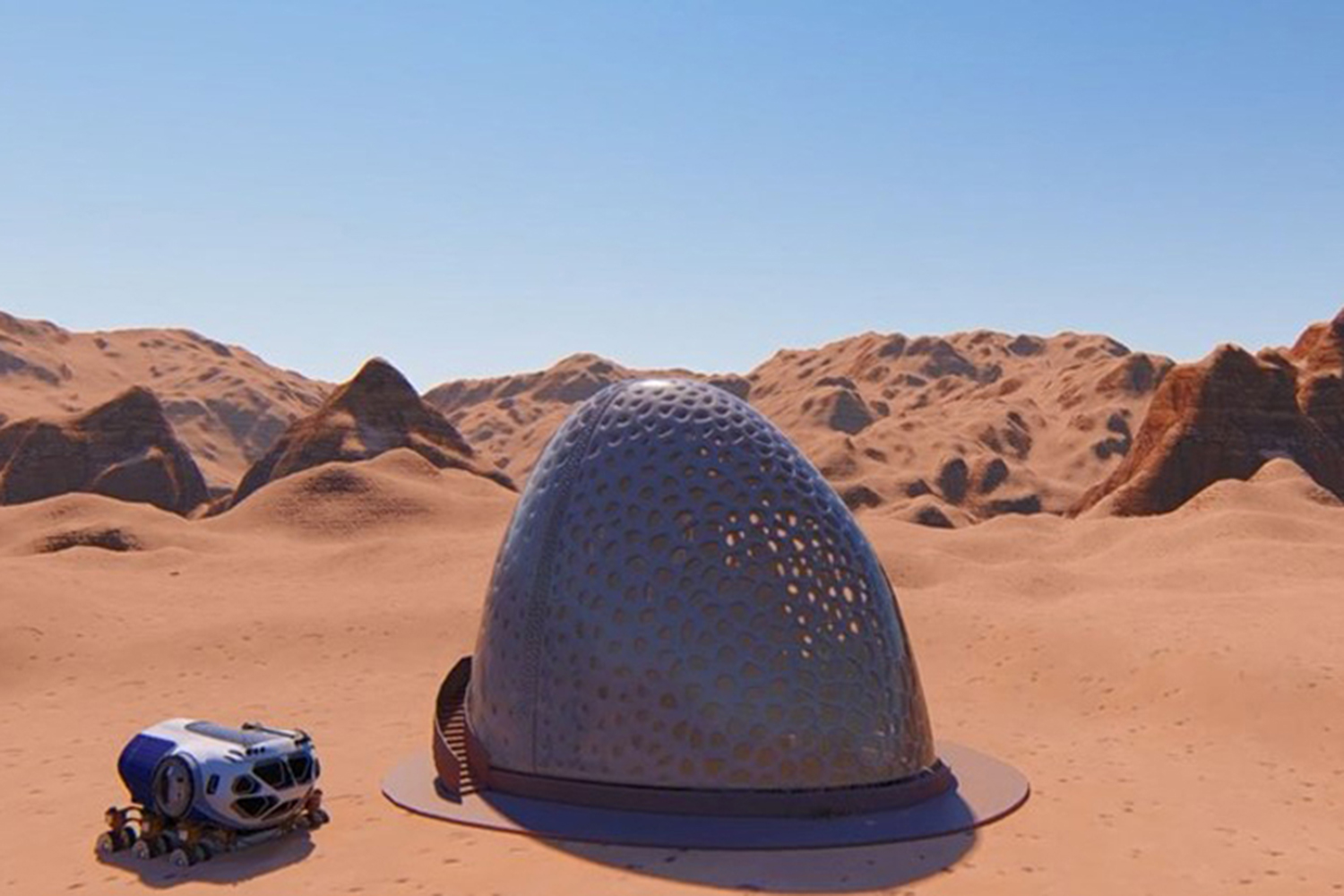
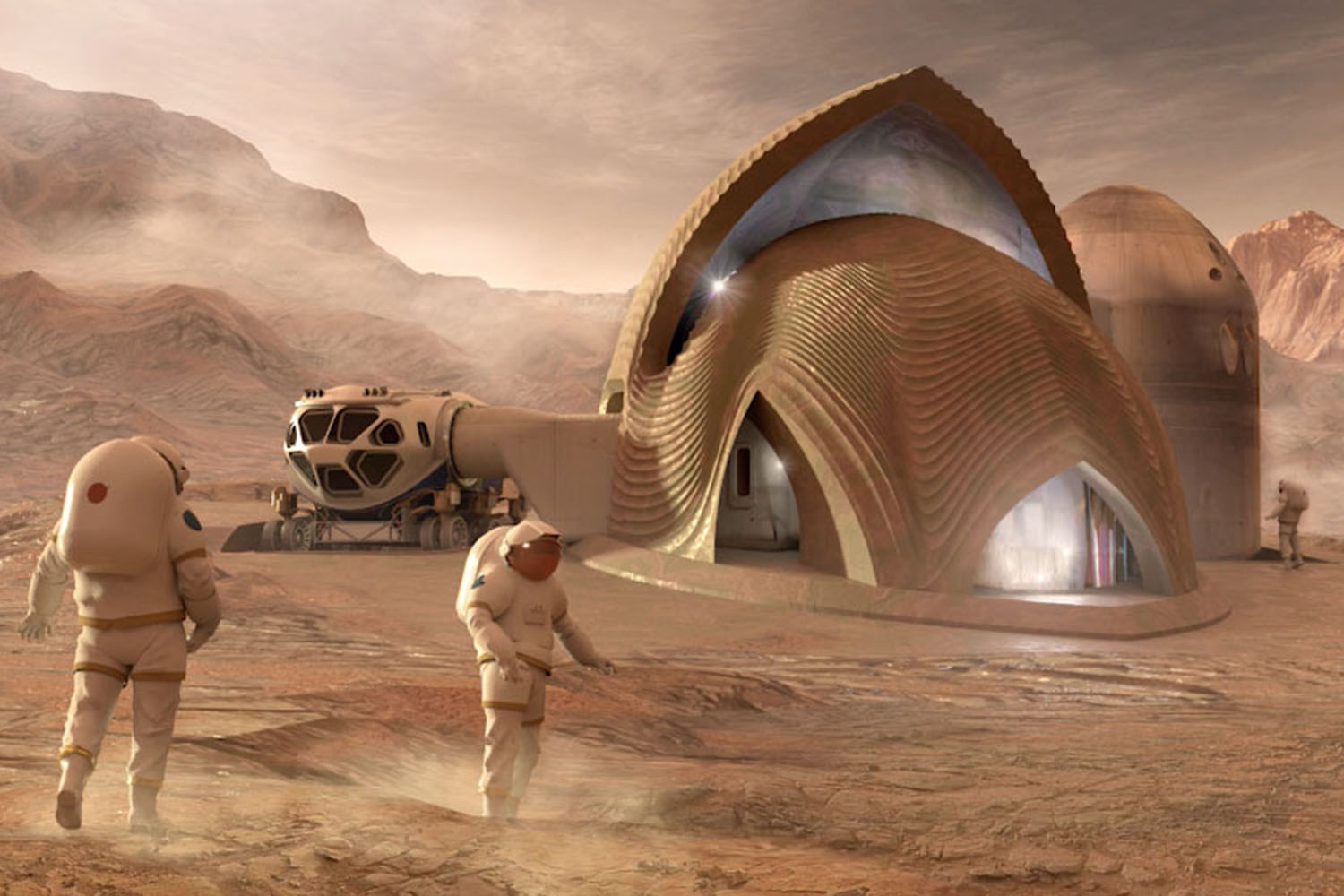
When astronauts finally touch down to establish a community on the moon or another planet, they will have to quickly erect unique structures to shelter them from the elements. The architectural design of these habitats will depend on their location, including what resources are available and what conditions are like outside. And, since it’s expensive to ship supplies into space, we’ll likely depend on 3D printing to fabricate the buildings with as much ease and local resources as possible.
To get a better understanding of what these structures might look like on Mars, NASA partnered with Bradley University in Peoria, Illinois for its 3D-Printed Habitat Centennial Challenge competition, which began in 2014. The first two phases included a design competition and structural competition. The five winners of the latest phase, which challenged the teams to design sub-scale habitats, were recently announced and will share in the $100,000 prizes.
“We are thrilled to see the success of this diverse group of teams that have approached this competition in their own unique styles,” Monsi Roman, program manager for NASA’s Centennial Challenges, said in a statement. “They are not just designing structures, they are designing habitats that will allow our space explorers to live and work on other planets. We are excited to see their designs come to life as the competition moves forward.”
The winning teams used digital tools to fabricate the physical and functional features of their Martian habitats, earning their lot of the prize money based on scores given to them by a panel of judges. Eighteen teams from around the world were considered. The five winning teams were:
1. Team Zopherus of Rogers, Arkansas – $20,957.95
2. AI. SpaceFactory of New York – $20,957.24
3. Kahn-Yates of Jackson, Mississippi – $20,622.74
4. SEArch+/Apis Cor of New York – $19,580.97
5. Northwestern University of Evanston, Illinois – $17,881.10
“We are encouraging a wide range of people to come up with innovative designs for how they envision a habitat on Mars,” Lex Akers, dean of the Caterpillar College of Engineering and Technology at Bradley University, said. “The virtual levels allow teams from high schools, universities, and businesses that might not have access to large 3D printers to still be a part of the competition because they can team up with those who do have access to such machinery for the final level of the competition.”
Editors' Recommendations
- NASA sets new target launch date for Starliner spacecraft
- NASA confirms readiness for highly anticipated crewed mission
- NASA to help with the launch of Europe’s unlucky Mars rover
- NASA’s Orion spacecraft has ‘critical issues’ with its heat shield, report finds
- NASA selects 9 companies to work on low-cost Mars projects